Drone Mapping


WORK SMART WITH DRONE DATA
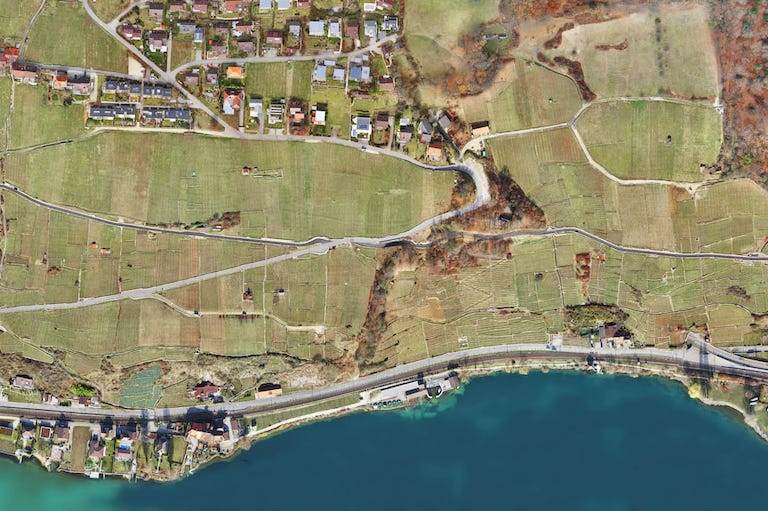
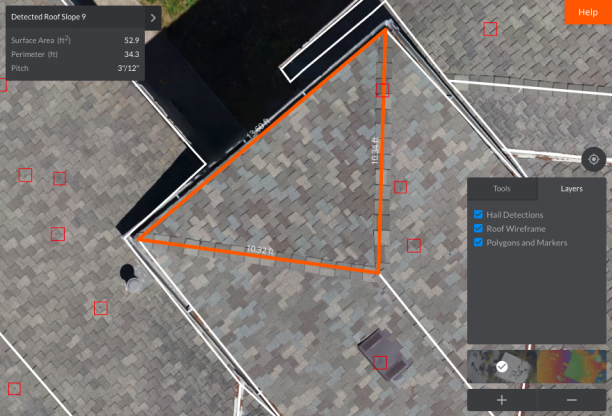
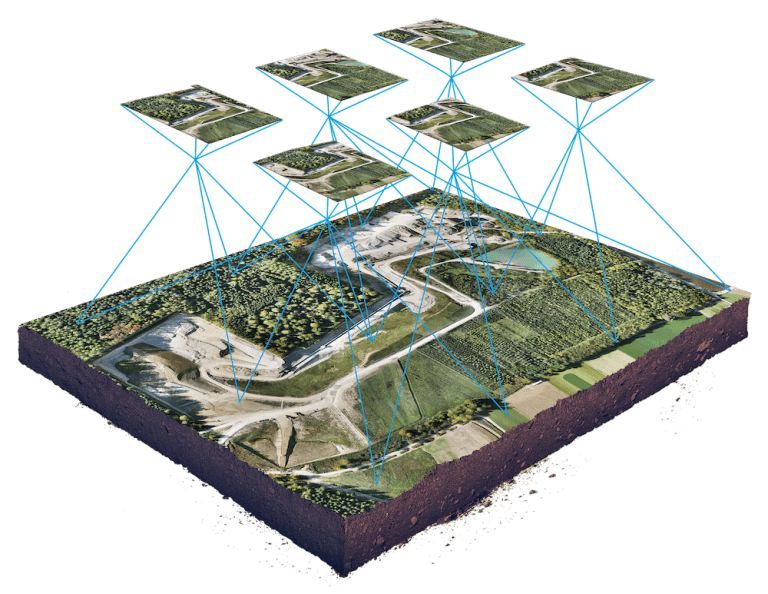
MAP WITHOUT LIMITS
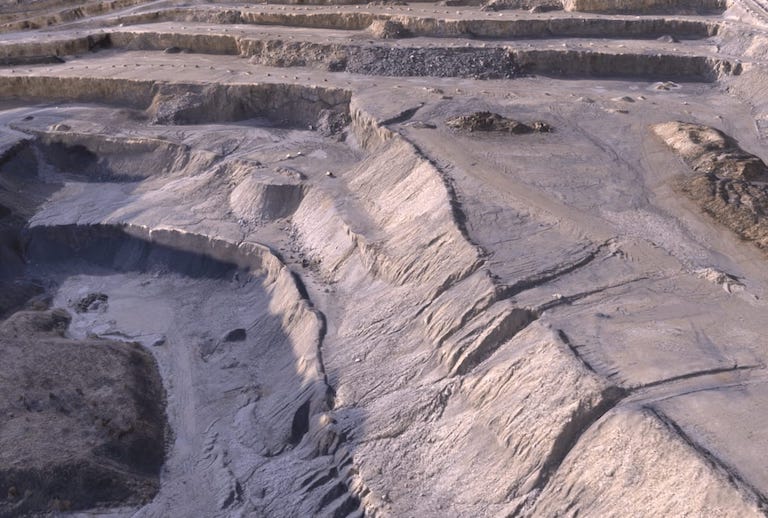
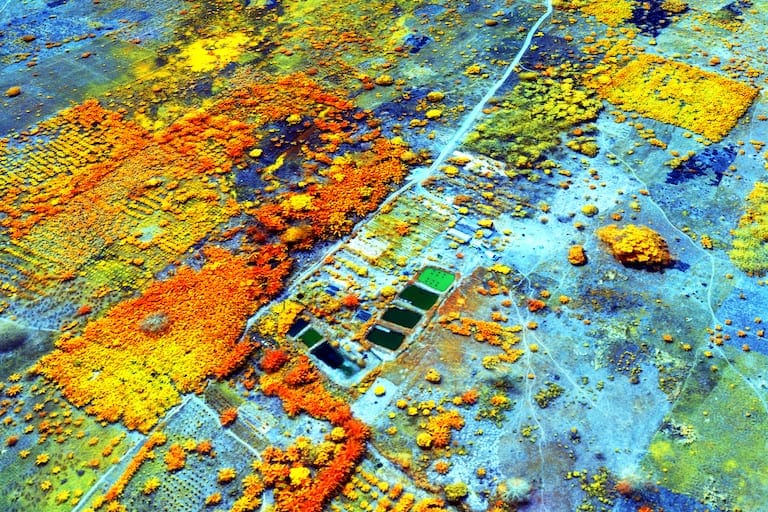
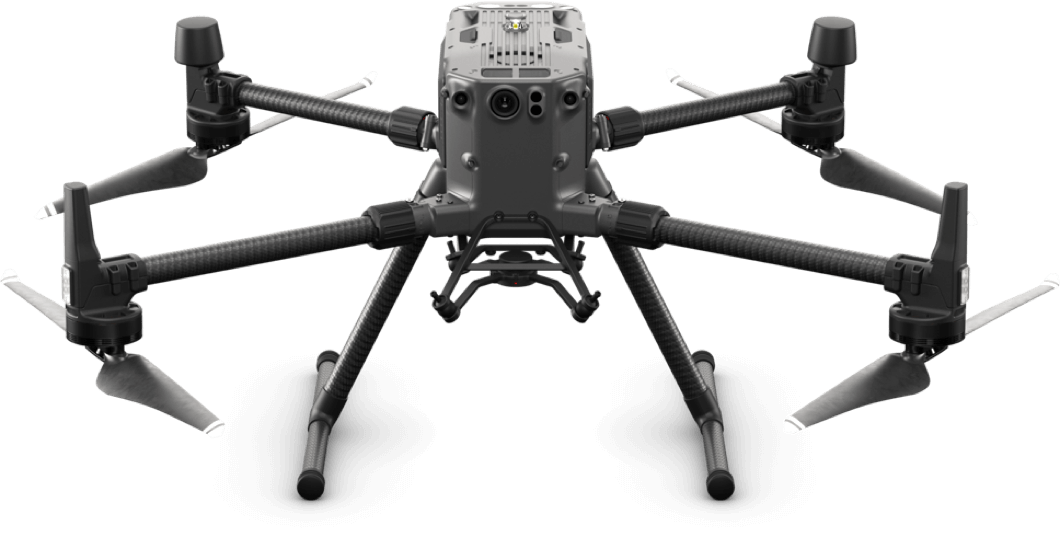
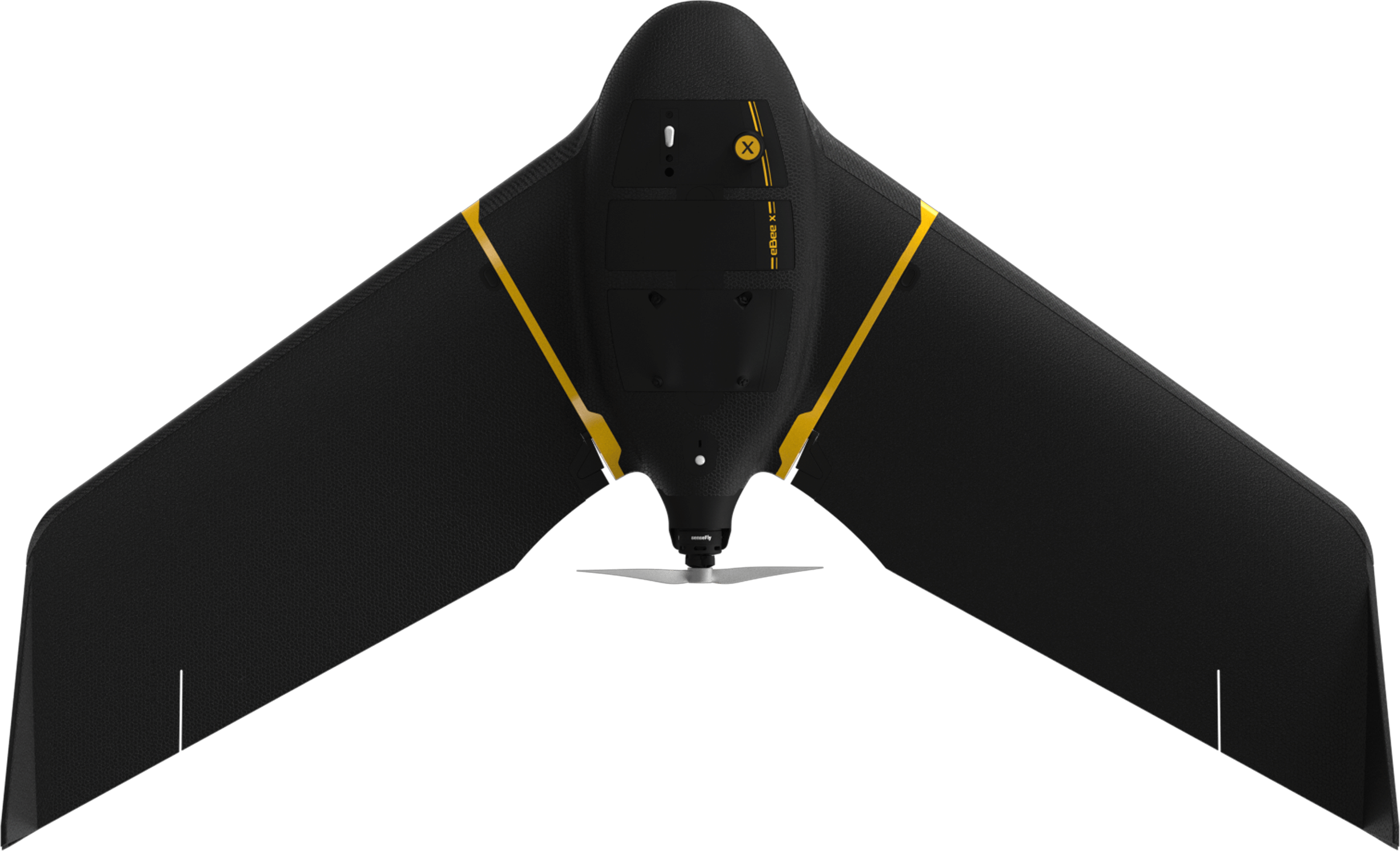
Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) By Martix 300 Drones and Ebee X Drone can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of your projects. By allowing easier access and capturing volumes of highly accurate data in less time, UAVs can reduce project costs. By allowing close-up inspection of hard-to-reach structures, rugged terrain, and remote sites, They can reduce risk. And by providing real-time project information and accurate side by side comparisons, they can facilitate informed decision making, improving project quality.